Frequency-Dependent Modelling
- Grid/electrode impedance Z(f) with ground return effects
- Skin & proximity effects on conductors and cable screens
- Realistic terminations, bonds and routing
GSA FD extends GSA with frequency-dependent behaviour of conductors and soil. Evaluate grid impedance versus frequency, induced voltages on adjacent systems, and screening/bonding effectiveness under harmonics and fast transients.
Accurate wideband earthing analysis with realistic coupling to nearby infrastructures.
| Area | Details |
|---|---|
| Physics & Modelling | Frequency-dependent parameters for conductors/soil including ground return; mutual couplings; realistic screen/sheath modelling and bonding layouts; impedance Z(f) and GPR(f). |
| Use Cases | Substations and plants with harmonics, traction & rail proximity, pipelines and telecom routes, HV earth electrodes, renewable plants and industrial campuses. |
| Inputs | Geometry and routing, multilayer soil models, bonding/terminations, operating and contingency scenarios, harmonic content or representative spectra. |
| Outputs | Grid impedance and apparent resistance vs frequency, GPR(f), induced voltages/currents, transfer potentials, screening effectiveness, and safety indicators across scenarios. |
| Integration | Shared workflow with GSA; complements XGSA FD/TD, NETS and SHIELD for system-level analysis and reporting. |
Need low-frequency only? Use GSA. For time-domain coupling, see XGSATD.
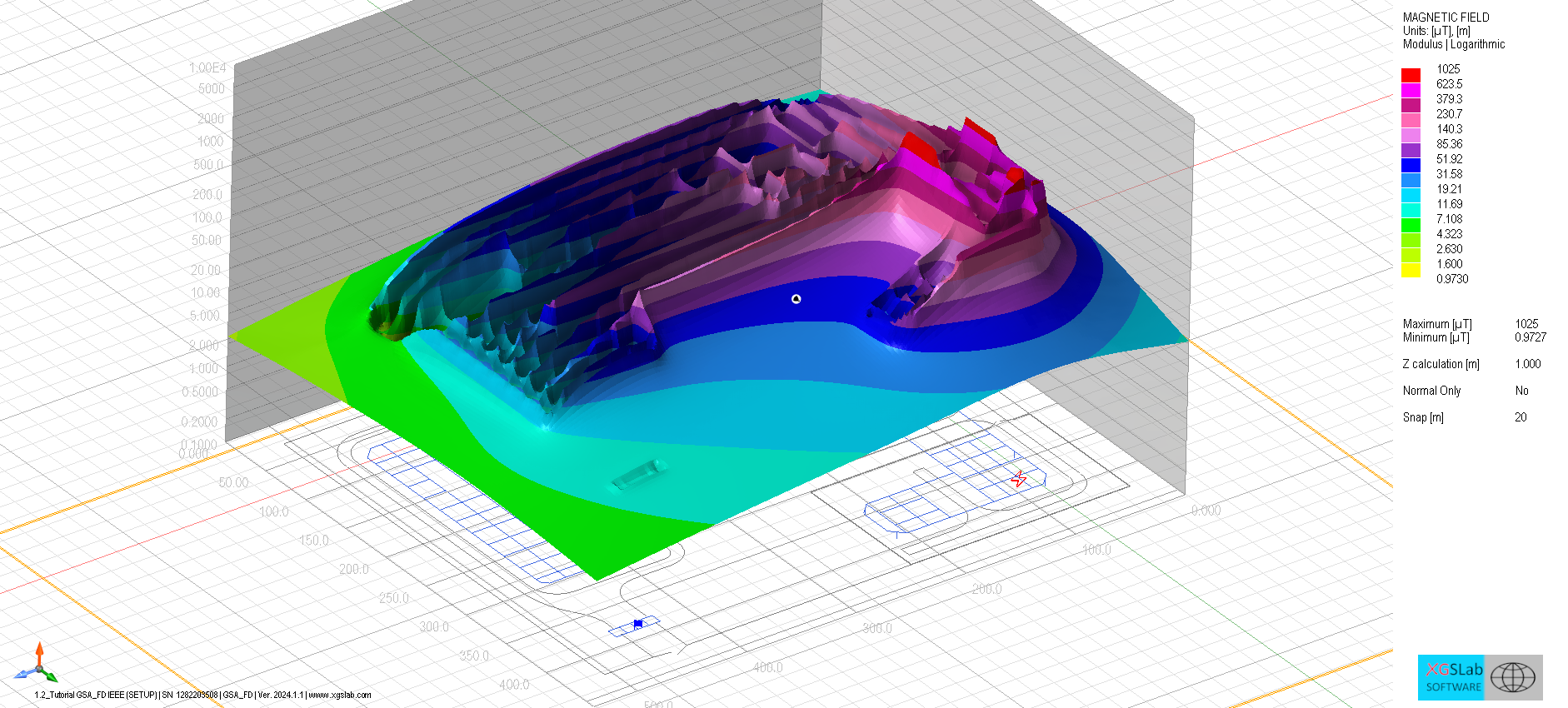
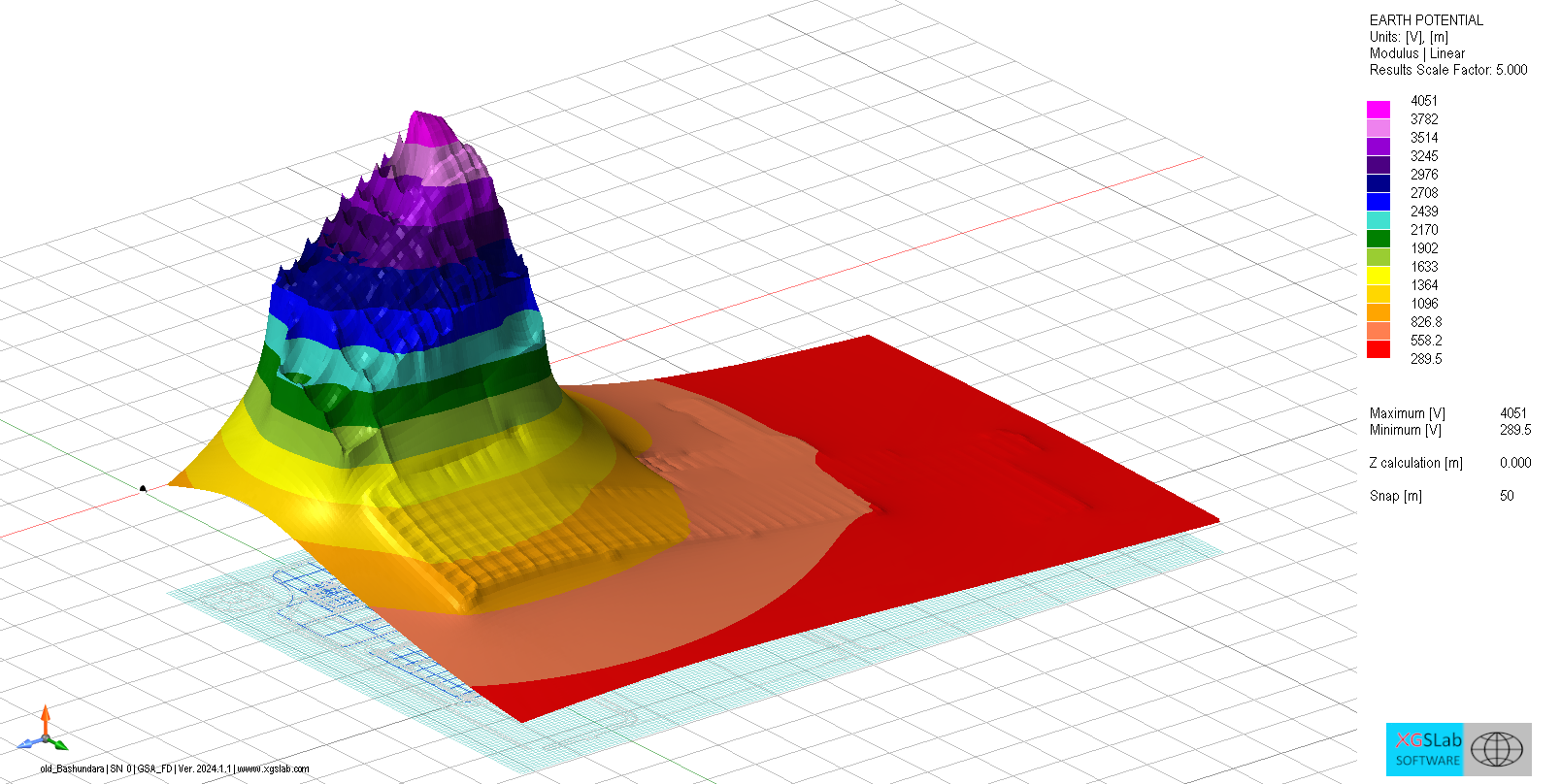
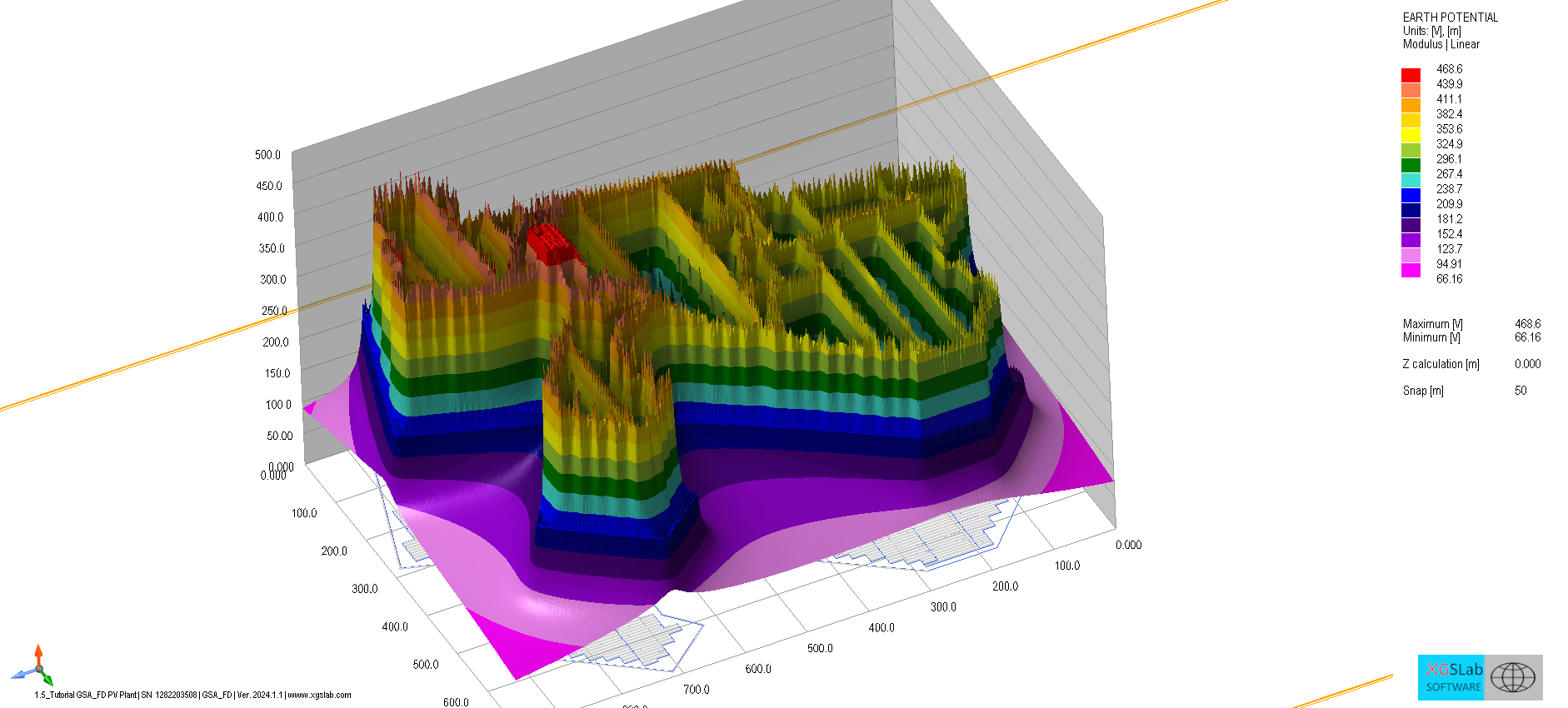
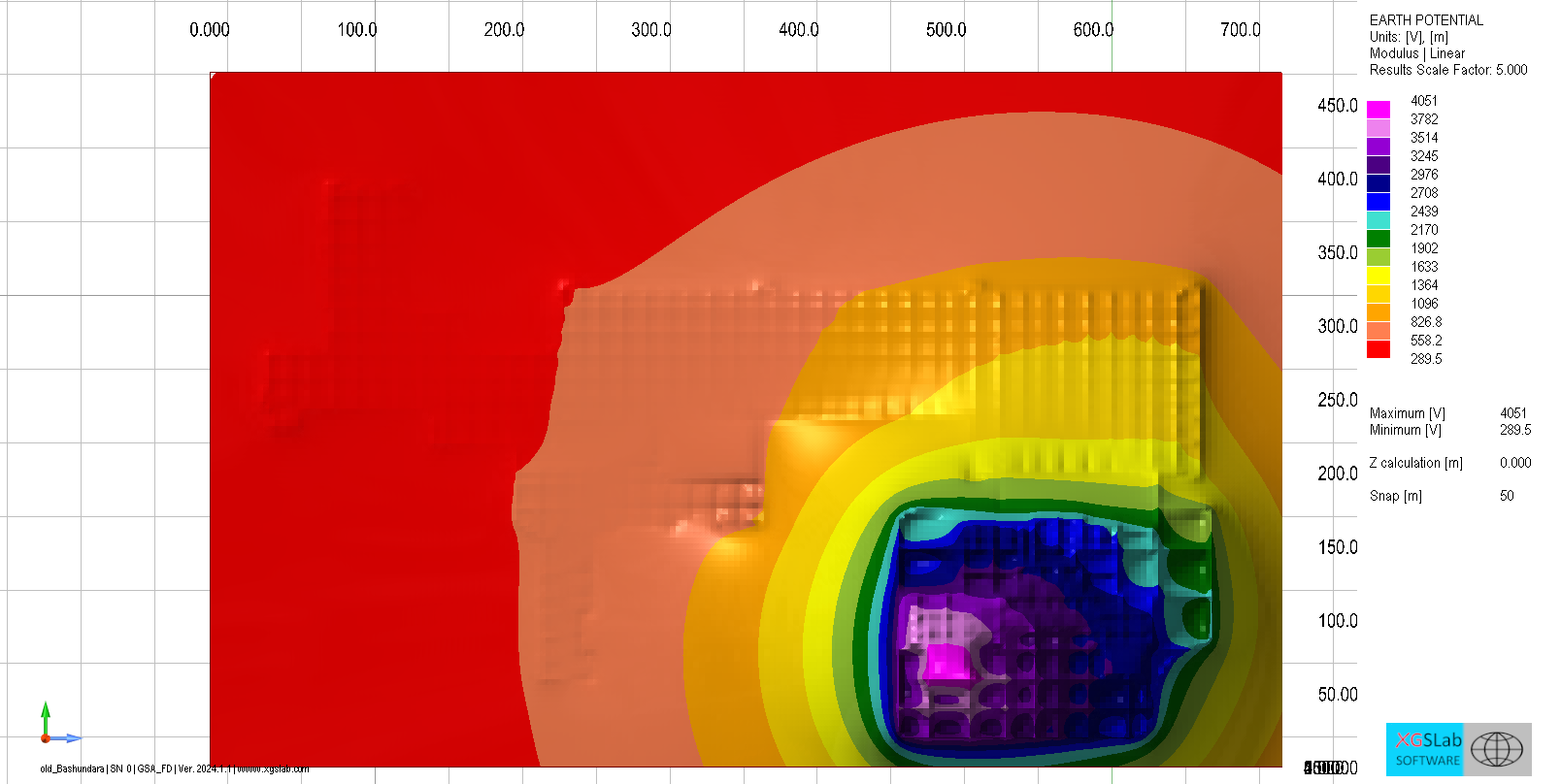
Define spectra and bonds, evaluate Z(f)/GPR(f), and verify coupling limits.
Frequency-dependent parameters, coupling paths, screening strategies.
Geometry, soil, bonds/terminations, operating scenarios, harmonic content.
Impedance & GPR vs frequency, induced V/I, transfer potentials.
Bonding/screen optimization, routing changes, surface layers and controls.
Use GSA FD when harmonics, wideband behaviour, or induced effects on nearby assets are important. For steady-state low-frequency only, GSA is typically sufficient.
Accurate soil stratification, realistic bonding and terminations, and representative harmonic spectra or envelopes for the operating cases.
Share your layout, bonds and spectra—our team will help you verify coupling risks and optimize mitigation.